| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
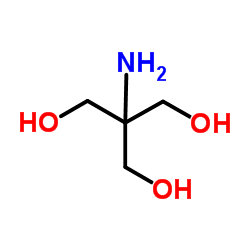 |
Trometamol
CAS:77-86-1 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
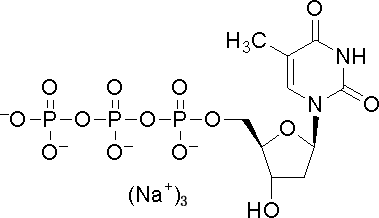 |
Deoxythymidine triphosphate
CAS:18423-43-3 |
|
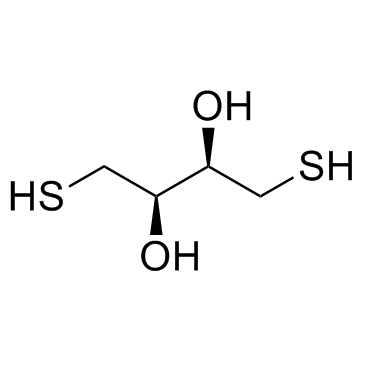 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |