| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
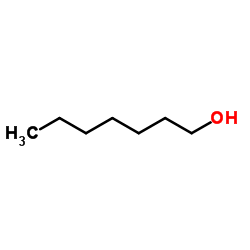 |
Heptan-1-ol
CAS:111-70-6 |
|
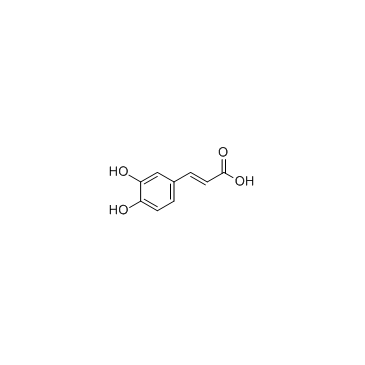 |
Caffeic acid
CAS:331-39-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
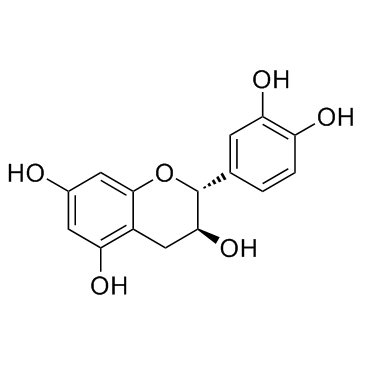 |
Catechin
CAS:154-23-4 |
|
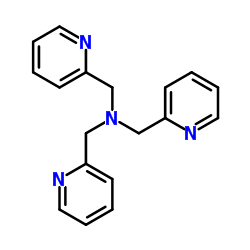 |
Tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine
CAS:16858-01-8 |