| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
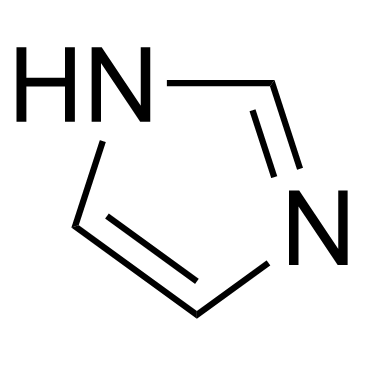 |
Imidazole
CAS:288-32-4 |
|
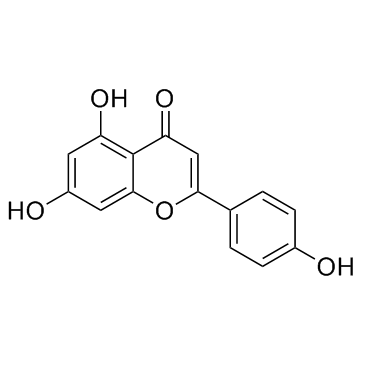 |
Apigenin
CAS:520-36-5 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
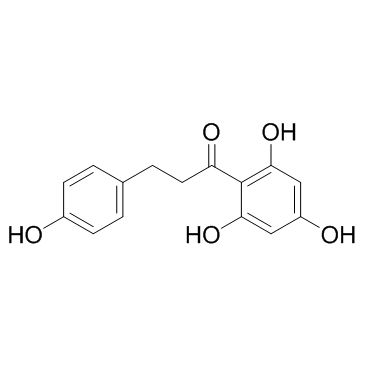 |
Phloretin
CAS:60-82-2 |
|
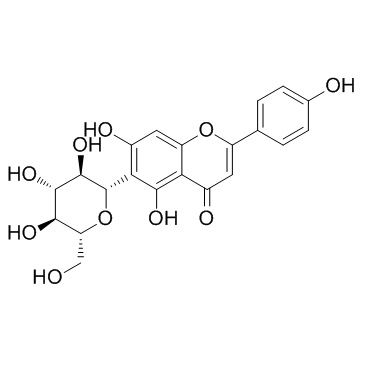 |
Isovitexin
CAS:38953-85-4 |
|
 |
(±)-Naringenin
CAS:67604-48-2 |