| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
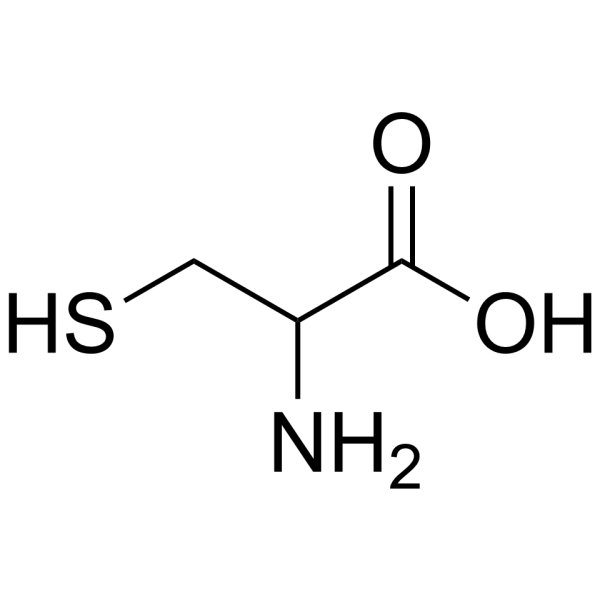 |
DL-CYSTEINE (1-13C)
CAS:3374-22-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
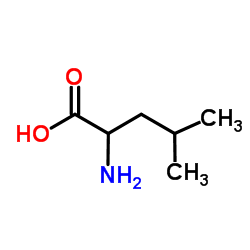 |
2-Amino-4-methylpentanoic acid
CAS:328-39-2 |
|
 |
DL-Methionine
CAS:59-51-8 |
|
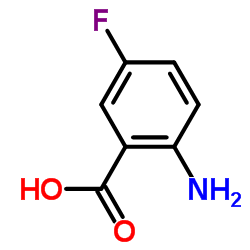 |
2-Amino-5-fluorobenzoic acid
CAS:446-08-2 |
|
 |
Uracil
CAS:66-22-8 |