| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Calcium
CAS:7440-70-2 |
|
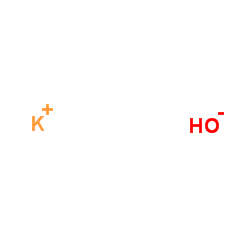 |
Potassium hydroxide
CAS:1310-58-3 |
|
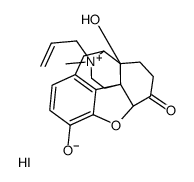 |
NALOXONE METHIODIDE
CAS:93302-47-7 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
H-D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Orn-Thr-Pen-Thr-NH2 trifluoroacetate salt (Disulfide bond)
CAS:103429-31-8 |
|
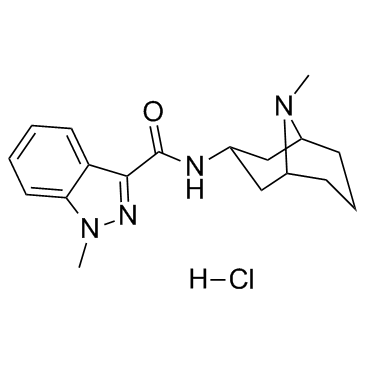 |
Granisetron hydrochloride
CAS:107007-99-8 |
|
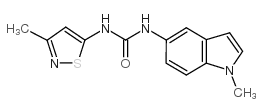 |
SB 204741
CAS:152239-46-8 |
|
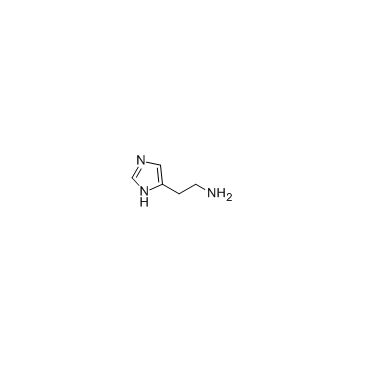 |
Histamine
CAS:51-45-6 |
|
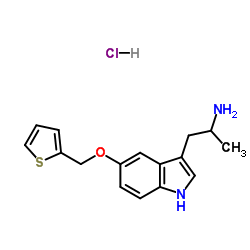 |
BW-723C86
CAS:160521-72-2 |