| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
 |
sodium dodecyl sulfate
CAS:151-21-3 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
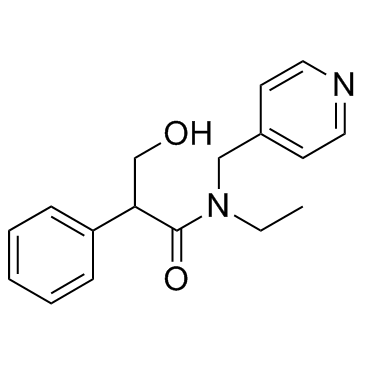 |
Tropicamide
CAS:1508-75-4 |
|
 |
Suplatast Tosilate
CAS:94055-76-2 |