| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sodium hydroxide
CAS:1310-73-2 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
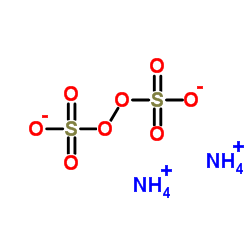 |
ammonium persulfate
CAS:7727-54-0 |
|
 |
3-Ethyl-2,4-pentanedione
CAS:1540-34-7 |
|
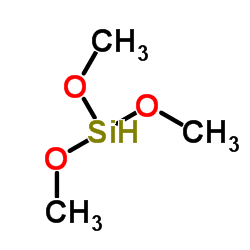 |
Trimethoxysilane
CAS:2487-90-3 |
|
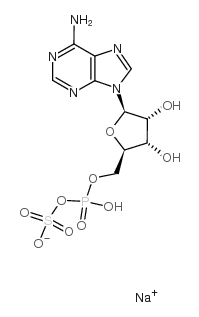 |
APS SODIUM SALT
CAS:102029-95-8 |