| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
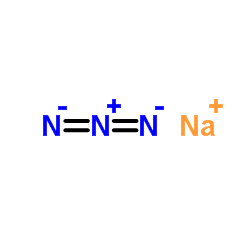 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
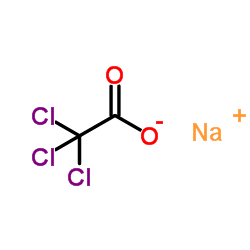 |
Sodium TCA
CAS:650-51-1 |
|
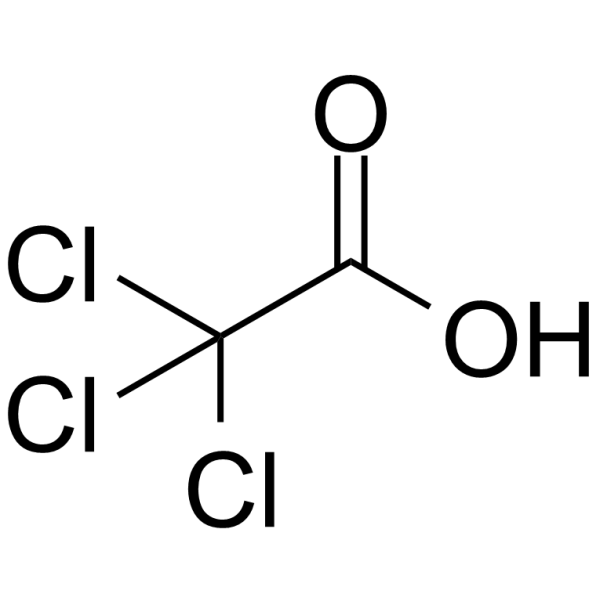 |
Trichloroacetic acid
CAS:76-03-9 |
|
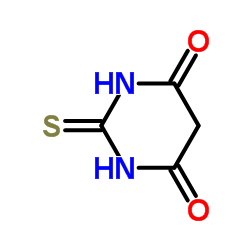 |
4,6-Dihydroxy-2-mercaptopyrimidine
CAS:504-17-6 |
|
 |
Tetraethoxypropane
CAS:122-31-6 |