| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
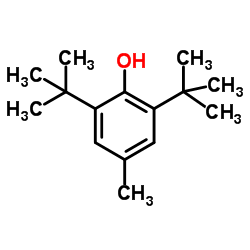 |
Butylated hydroxytoluene
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
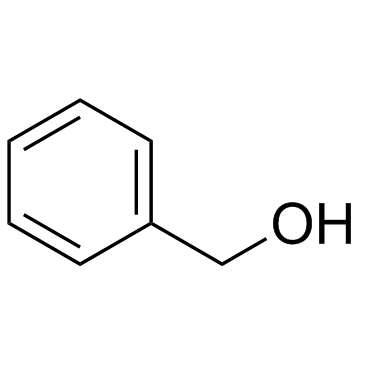 |
Benzyl alcohol
CAS:100-51-6 |
|
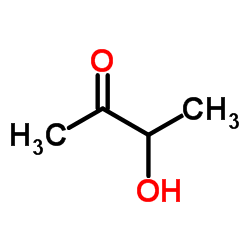 |
Acetoin
CAS:513-86-0 |
|
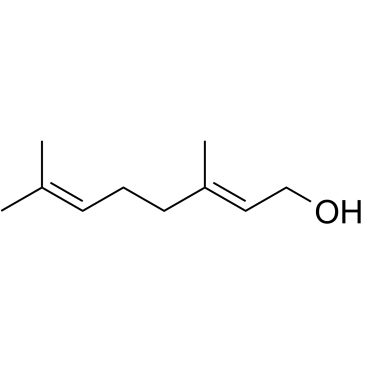 |
Geraniol
CAS:106-24-1 |
|
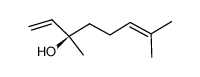 |
(-)-Linalool
CAS:126-91-0 |
|
 |
cis-3,7-Dimethyl-2,6-octadien-1-ol
CAS:106-25-2 |
|
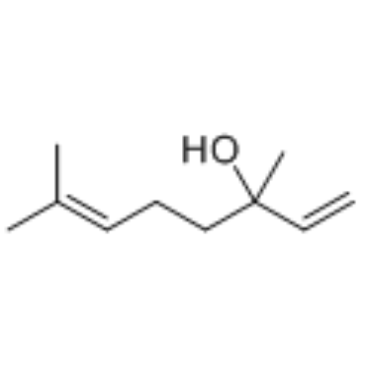 |
Linalool
CAS:78-70-6 |