| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
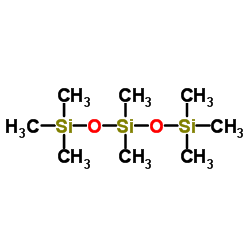 |
Octamethyltrisiloxane
CAS:107-51-7 |
|
 |
Hexamethyldisiloxane
CAS:107-46-0 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
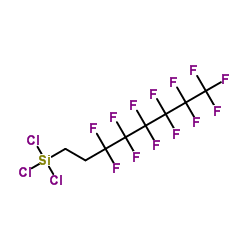 |
1h,1h,2h,2h-perfluorooctyltrichlorosilane
CAS:78560-45-9 |
|
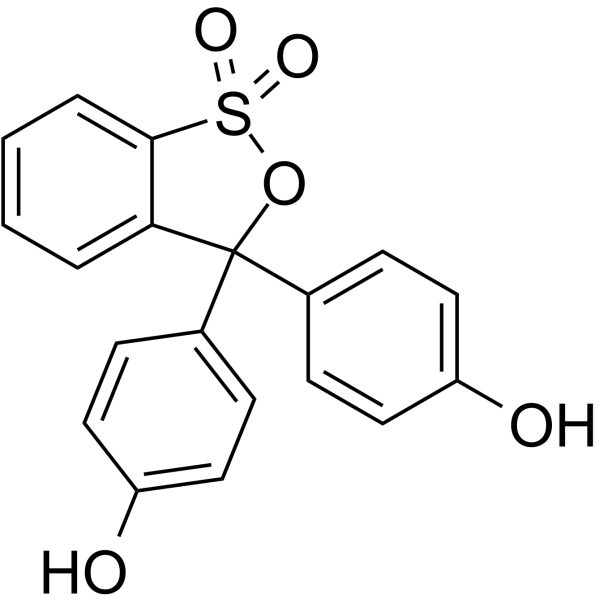 |
Phenol red
CAS:143-74-8 |