| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
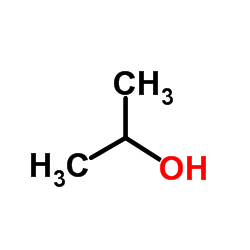 |
Isopropanol
CAS:67-63-0 |
|
 |
alpha-Quarterthiophene
CAS:5632-29-1 |
|
 |
2,2'-(perfluorocyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-diylidene)dimalononitrile
CAS:29261-33-4 |
|
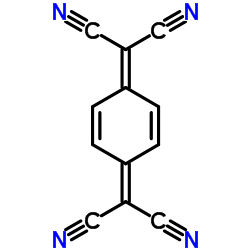 |
Tetracyanoquinodimethane
CAS:1518-16-7 |