| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
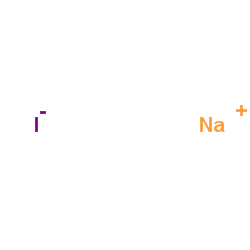 |
Sodium iodide
CAS:7681-82-5 |
|
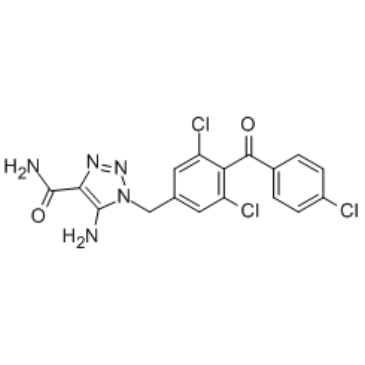 |
L-651,582
CAS:99519-84-3 |
|
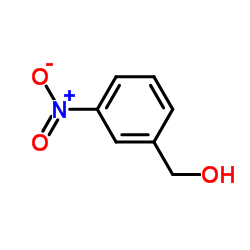 |
3-Nitrobenzenemethanol
CAS:619-25-0 |