| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Dimethyl sulfoxide
CAS:67-68-5 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
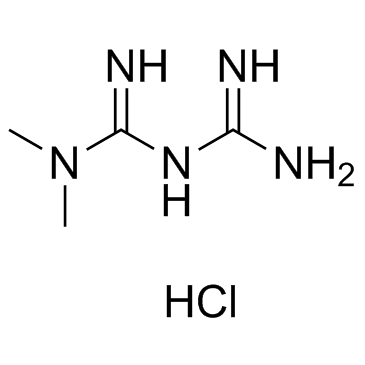 |
Metformin HCl
CAS:1115-70-4 |
|
 |
Tween 20
CAS:9005-64-5 |
|
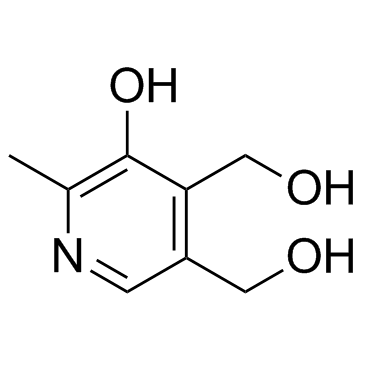 |
Pyridoxine
CAS:65-23-6 |
|
 |
Genistein
CAS:446-72-0 |
|
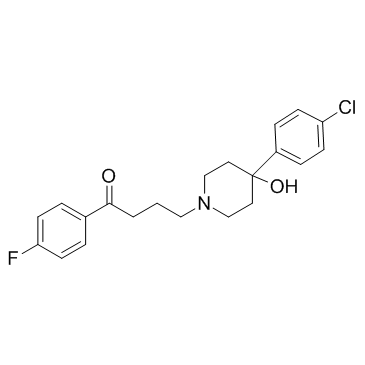 |
haloperidol
CAS:52-86-8 |
|
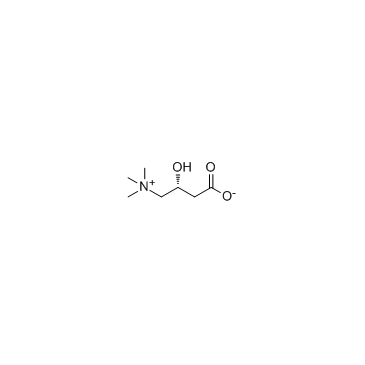 |
L-Carnitine inner salt
CAS:541-15-1 |
|
 |
TMS
CAS:75-76-3 |