| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Potassium bromide
CAS:7758-02-3 |
|
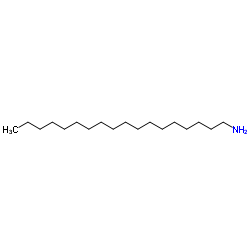 |
Octadecanamine
CAS:124-30-1 |
|
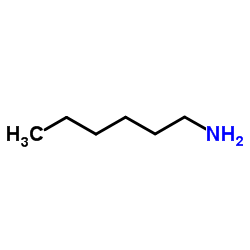 |
Hexylamine
CAS:111-26-2 |
|
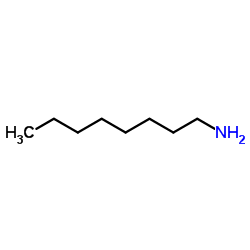 |
Octylamine
CAS:111-86-4 |
|
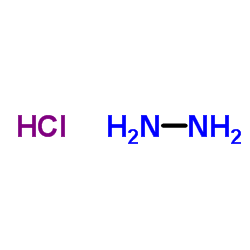 |
Hydrazine hydrochloride
CAS:2644-70-4 |
|
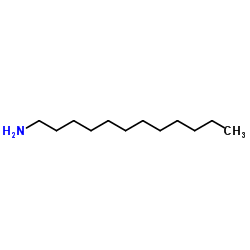 |
Dodecanamine
CAS:124-22-1 |
|
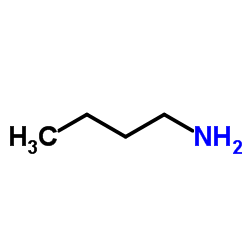 |
n-butylamine
CAS:109-73-9 |