| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
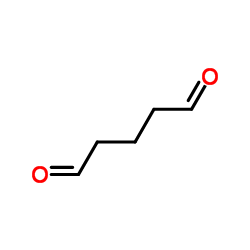 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
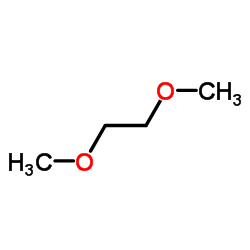 |
1,2-dimethoxyethane
CAS:110-71-4 |