| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
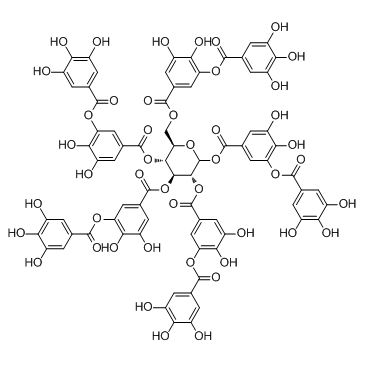 |
Tannic acid
CAS:1401-55-4 |
|
 |
Chloroform
CAS:67-66-3 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
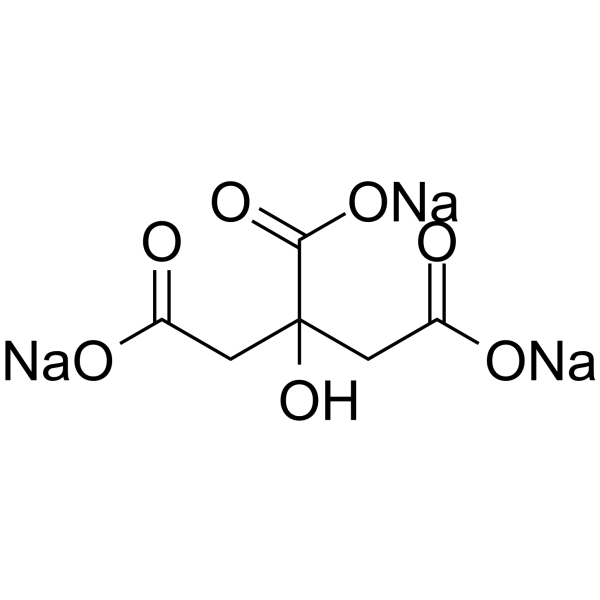 |
Sodium citrate
CAS:68-04-2 |
|
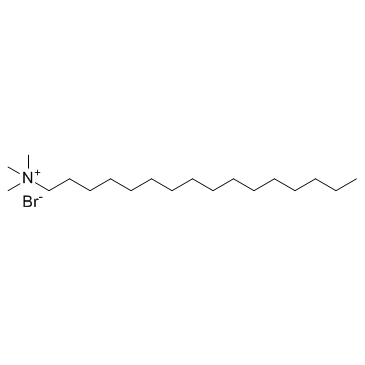 |
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
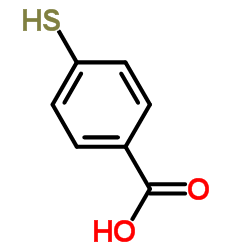 |
4-mercaptobenzoic acid
CAS:1074-36-8 |
|
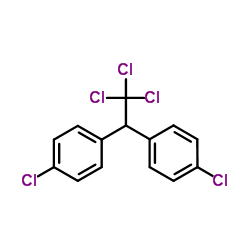 |
DDT
CAS:50-29-3 |
|
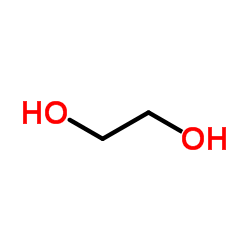 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |
|
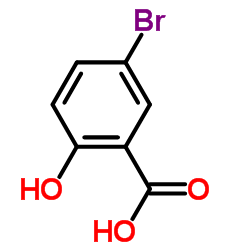 |
5-Bromo-2-hydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:89-55-4 |
|
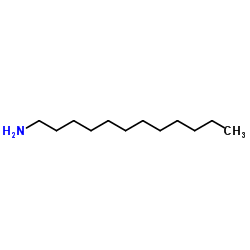 |
Dodecanamine
CAS:124-22-1 |