| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Crotonic acid
CAS:107-93-7 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
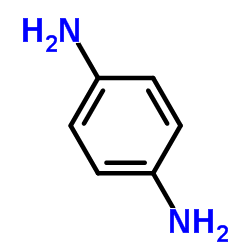 |
p-Phenylenediamine
CAS:106-50-3 |
|
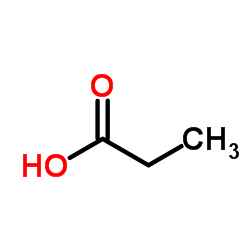 |
Propionic acid
CAS:79-09-4 |
|
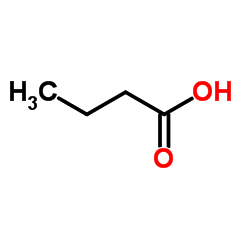 |
Butyric Acid
CAS:107-92-6 |
|
 |
Acrylic acid
CAS:79-10-7 |
|
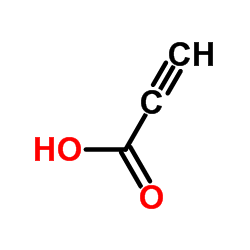 |
Propiolic acidd
CAS:471-25-0 |