| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
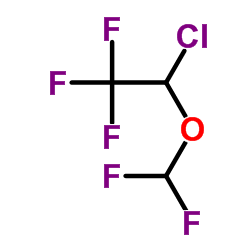 |
Isoflurane
CAS:26675-46-7 |
|
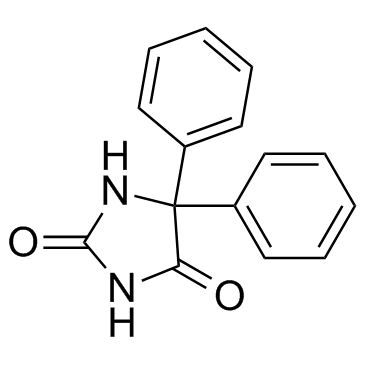 |
phenytoin
CAS:57-41-0 |
|
 |
Atenolol
CAS:29122-68-7 |
|
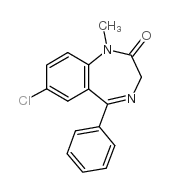 |
diazepam
CAS:439-14-5 |
|
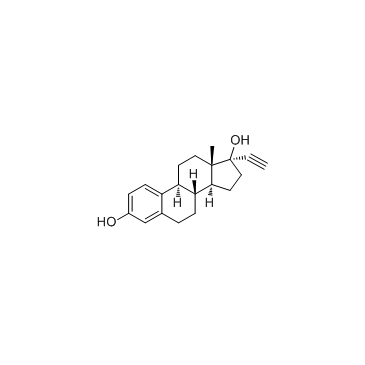 |
Ethynyl estradiol
CAS:57-63-6 |
|
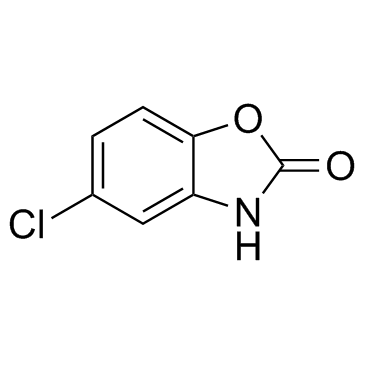 |
Chlorzoxazone
CAS:95-25-0 |