| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
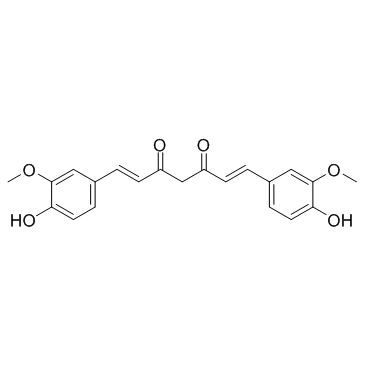 |
Curcumin
CAS:458-37-7 |
|
 |
sucrose
CAS:57-50-1 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
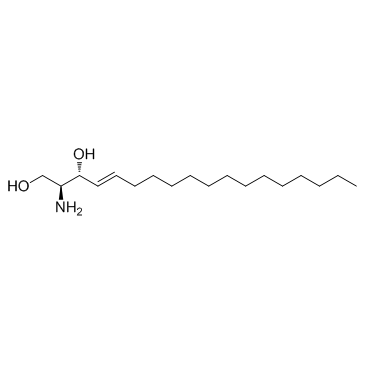 |
D-erythro-Sphingosine
CAS:123-78-4 |
|
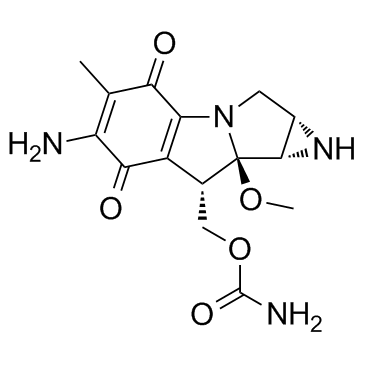 |
Mitomycin C
CAS:50-07-7 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
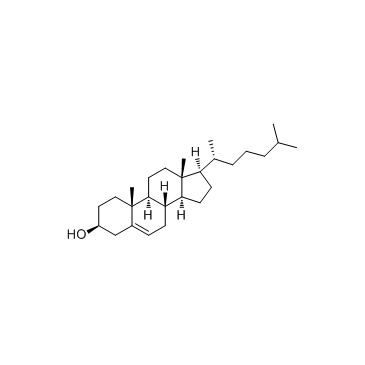 |
cholesterol
CAS:57-88-5 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |