| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
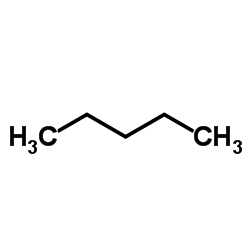 |
Pentane
CAS:109-66-0 |
|
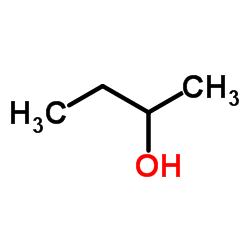 |
(±)-2-Butanol
CAS:78-92-2 |
|
 |
UNII:FE7IK35OPN
CAS:2269-22-9 |
|
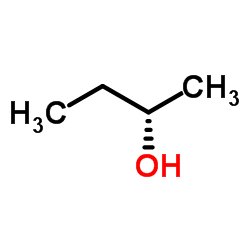 |
(S)-(+)-2-Butanol
CAS:4221-99-2 |
|
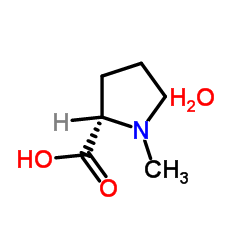 |
(R)-(-)-2-Butanol
CAS:14898-79-4 |