| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium carbonate
CAS:497-19-8 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
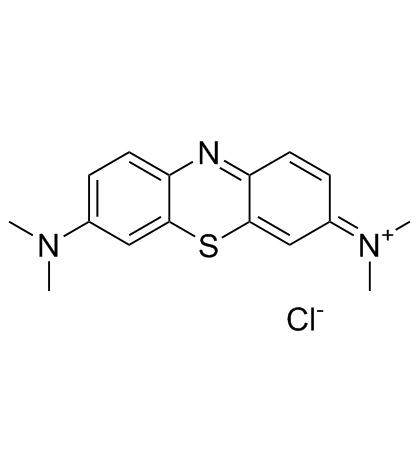 |
Methylene Blue
CAS:61-73-4 |
|
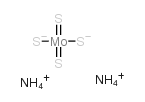 |
AMMONIUM TETRATHIOMOLYBDATE
CAS:15060-55-6 |
|
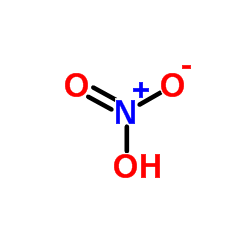 |
nitric acid
CAS:7697-37-2 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
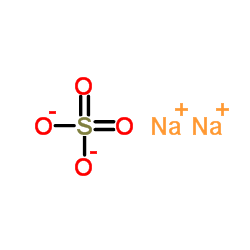 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Potassium
CAS:7440-09-7 |
|
 |
Ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate
CAS:12054-85-2 |
|
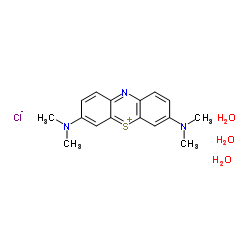 |
Methylene Blue trihydrate
CAS:7220-79-3 |