| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium carbonate
CAS:497-19-8 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
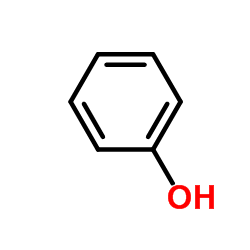 |
Phenol
CAS:108-95-2 |
|
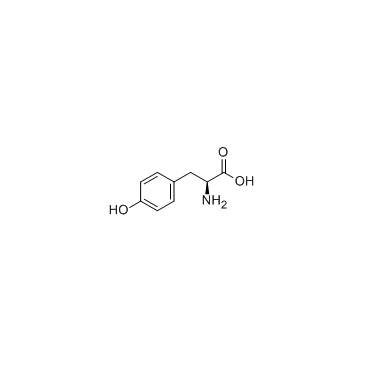 |
L-Tyrosine
CAS:60-18-4 |
|
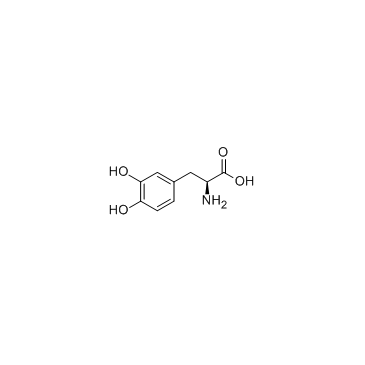 |
Levodopa
CAS:59-92-7 |
|
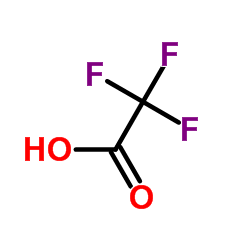 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |
|
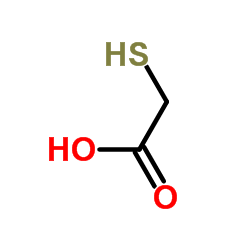 |
Mercaptoacetic acid
CAS:68-11-1 |
|
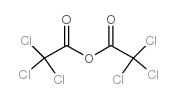 |
TRICHLOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE
CAS:4124-31-6 |
|
 |
argon-40
CAS:1290046-39-7 |