| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
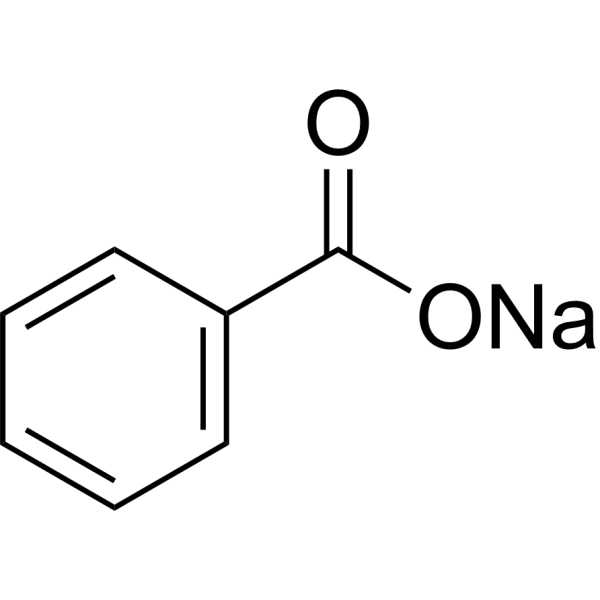 |
Sodium Benzoate
CAS:532-32-1 |
|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
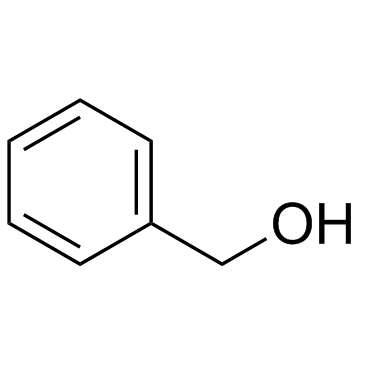 |
Benzyl alcohol
CAS:100-51-6 |
|
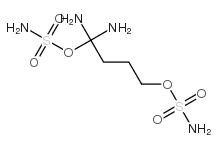 |
tetramine
CAS:80-12-6 |
|
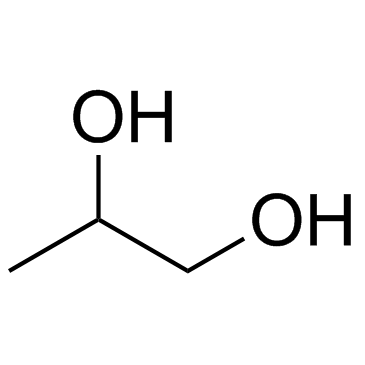 |
Propylene Glycol
CAS:57-55-6 |
|
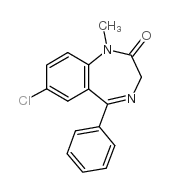 |
diazepam
CAS:439-14-5 |
|
 |
Sulfamide
CAS:7803-58-9 |
|
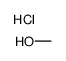 |
HYDROGEN CHLORIDE ~1.25 M IN METHANOL, 250 ML
CAS:132228-87-6 |