| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
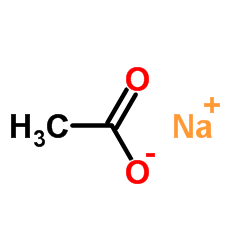 |
Sodium acetate
CAS:127-09-3 |
|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
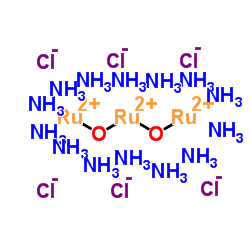 |
Ruthenium red
CAS:11103-72-3 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |