| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethidium bromide
CAS:1239-45-8 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
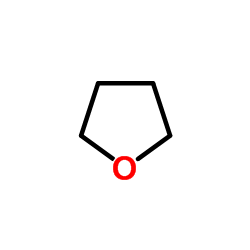 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
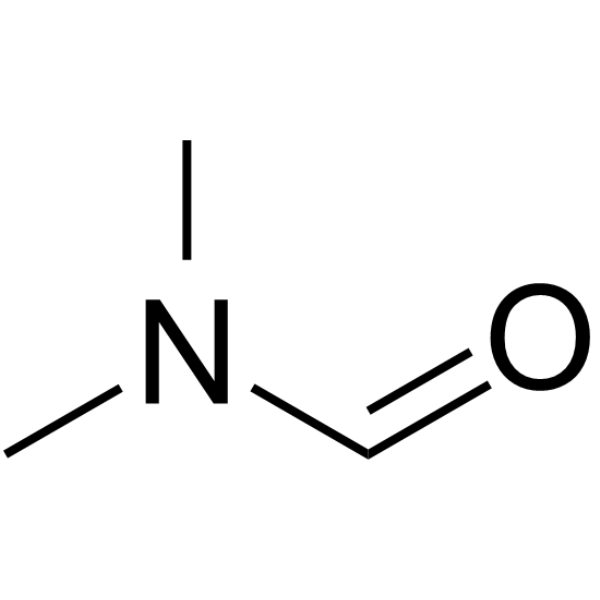 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
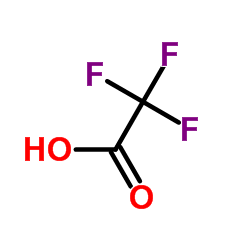 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
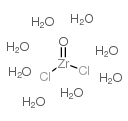 |
Zirconyl chloride octahydrate
CAS:13520-92-8 |
|
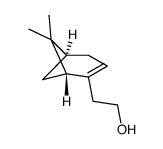 |
(-)-NOPOL
CAS:35836-73-8 |
|
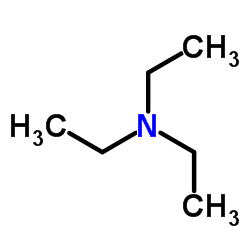 |
Triethylamine
CAS:121-44-8 |
|
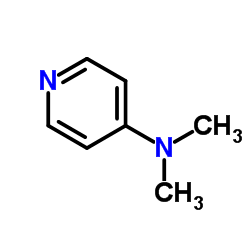 |
4-Dimethylaminopyridine
CAS:1122-58-3 |