| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
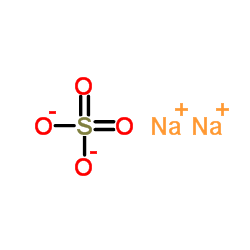 |
sodium sulfate
CAS:7757-82-6 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
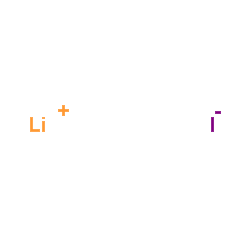 |
Lithium iodide
CAS:10377-51-2 |