| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
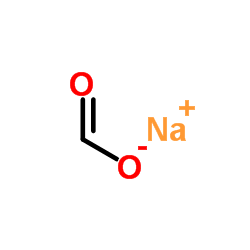 |
Sodium formate
CAS:141-53-7 |
|
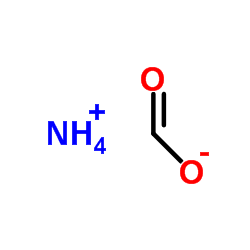 |
Formic acid ammonium salt
CAS:540-69-2 |
|
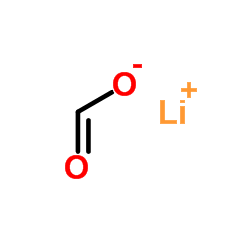 |
Lithium formate
CAS:556-63-8 |
|
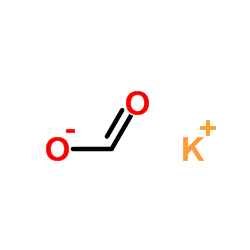 |
Potassium formate
CAS:590-29-4 |
|
 |
Formic acid, magnesiumsalt (2:1)
CAS:557-39-1 |
|
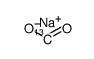 |
Formate-13C sodium
CAS:23102-86-5 |
|
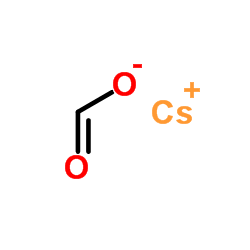 |
Caesium formate
CAS:3495-36-1 |
|
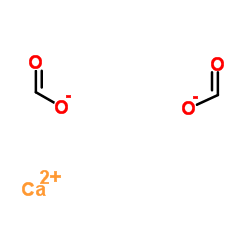 |
Calcium diformate
CAS:544-17-2 |