| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
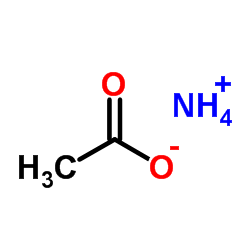 |
Ammonium acetate
CAS:631-61-8 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
 |
D-Biotin
CAS:58-85-5 |
|
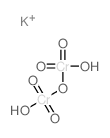 |
Potassium dichromate solution
CAS:7778-50-9 |
|
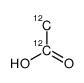 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
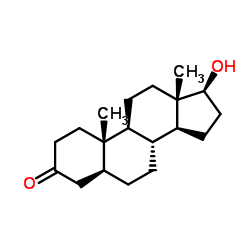 |
Stanolone
CAS:521-18-6 |
|
 |
Chrysene
CAS:218-01-9 |