| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
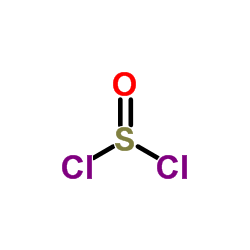 |
Thionyl chloride
CAS:7719-09-7 |
|
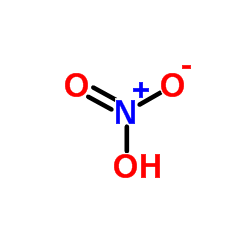 |
nitric acid
CAS:7697-37-2 |
|
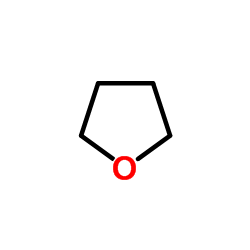 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
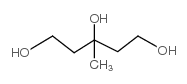 |
3-Methylpentane-1,3,5-triol
CAS:7564-64-9 |