| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
sodiumborohydride
CAS:16940-66-2 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
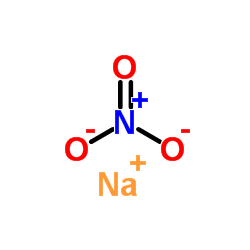 |
sodium nitrate
CAS:7631-99-4 |