| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
HYDROFLUORIC ACID
CAS:7664-39-3 |
|
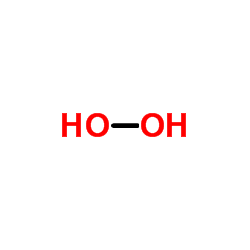 |
Hydrogen peroxide
CAS:7722-84-1 |
|
 |
Aqueous ammonia
CAS:1336-21-6 |
|
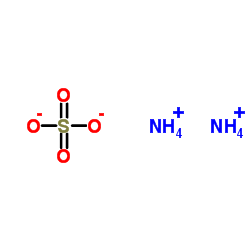 |
ammonium sulphate
CAS:7783-20-2 |
|
 |
sodium dihydrogenphosphate
CAS:7558-80-7 |
|
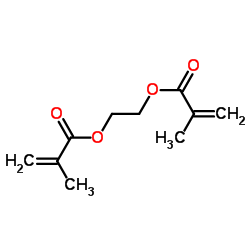 |
Ethylene methacrylate
CAS:97-90-5 |
|
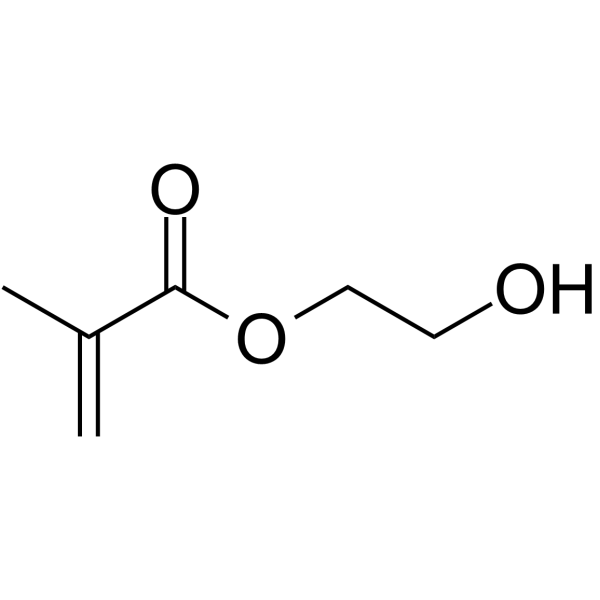 |
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate
CAS:868-77-9 |