| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Sulfuric acid
CAS:7664-93-9 |
|
 |
Salicylic acid
CAS:69-72-7 |
|
 |
Ethanoic anhydride
CAS:108-24-7 |
|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
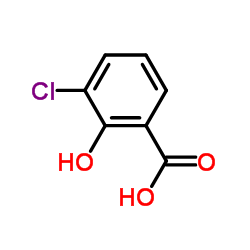 |
3-Chloro-2-hydroxybenzoic acid
CAS:1829-32-9 |