| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Glycerol
CAS:56-81-5 |
|
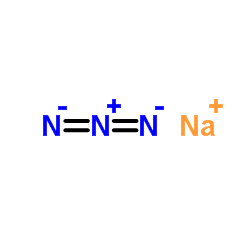 |
Sodium azide
CAS:26628-22-8 |
|
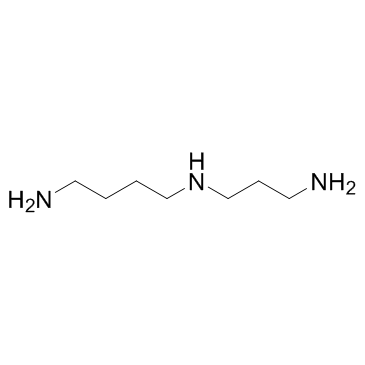 |
spermidine
CAS:124-20-9 |
|
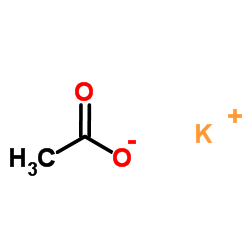 |
Potassium acetate
CAS:127-08-2 |
|
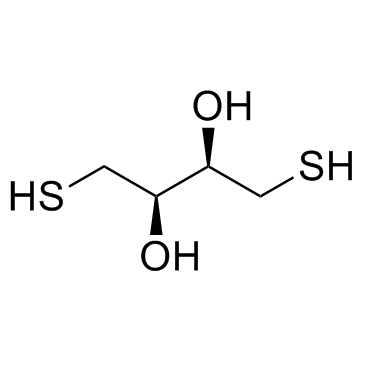 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |