蔗糖磷酸化酶
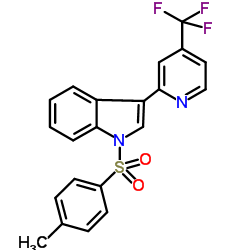
蔗糖磷酸化酶结构式

|
常用名 | 蔗糖磷酸化酶 | 英文名 | SUCROSE PHOSPHORYLASE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 9074-06-0 | 分子量 | 416.416 | |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 584.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C21H15F3N2O2S | 熔点 | N/A | |
| MSDS | 美版 | 闪点 | 307.0±32.9 °C |
蔗糖磷酸化酶用途蔗糖磷酸化酶是一种细菌转葡糖苷酶,催化蔗糖和磷酸盐转化为α-D-葡萄糖-1-磷酸和D-果糖。葡糖基化的蔗糖磷酸化酶也可以水解成α-D-葡萄糖,或将葡糖基转移到受体的羟基,然后分解成新的α-D-葡萄糖苷产物。碱性磷酸化酶对底物和产物的酶活性较弱[1]。 |
| 中文名 | 蔗糖磷酸化酶 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | 1-[(4-Methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]-1H-indole |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 描述 | 蔗糖磷酸化酶是一种细菌转葡糖苷酶,催化蔗糖和磷酸盐转化为α-D-葡萄糖-1-磷酸和D-果糖。葡糖基化的蔗糖磷酸化酶也可以水解成α-D-葡萄糖,或将葡糖基转移到受体的羟基,然后分解成新的α-D-葡萄糖苷产物。碱性磷酸化酶对底物和产物的酶活性较弱[1]。 |
|---|---|
| 相关类别 | |
| 参考文献 |
| 密度 | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 584.0±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 分子式 | C21H15F3N2O2S |
| 分子量 | 416.416 |
| 闪点 | 307.0±32.9 °C |
| 精确质量 | 416.080627 |
| LogP | 5.56 |
| 外观性状 | 冻干粉 |
| 蒸汽压 | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.610 |
| 储存条件 | -20°C密闭,避光,通风干燥处 |
| 稳定性 | Biochem/physiol Actions Enzymatically converts sucrose to D-fructose and D-glucose 1-phosphate. Unit Definition One unit will produce 1.0 μmole of D-fructose from sucrose per min with the corresponding reduction of NADP to NADPH at pH 7.6, at 25 °C . Physical form Contains sucrose as stabilizer. |
| 计算化学 | 计算化学数据: 1、 疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):3.2 2、 氢键供体数量:1 3、 氢键受体数量:2 4、 可旋转化学键数量:0 5、 拓扑分子极性表面积(TPSA):38.9 6、 重原子数量:18 7、 表面电荷:0 8、 复杂度:316 9、 同位素原子数量:0 10、 确定原子立构中心数量:0 11、 不确定原子立构中心数量:0 12、 确定化学键立构中心数量:0 13、 不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14、 共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:冻干粉末。 2. 密度(g/mL, 20 ℃ ):未确定 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):未确定 4. 熔点(ºC):未确定 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):未确定 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa):未确定 7. 折射率:未确定 8. 闪点(ºC):未确定 9. 比旋光度(º):未确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):未确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,20ºC):未确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):未确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):未确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):未确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):未确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:未确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):未确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):未确定 19. 溶解性:溶于水 |
| 危险品运输编码 | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|
|
Positively charged mini-protein Zbasic2 as a highly efficient silica binding module: opportunities for enzyme immobilization on unmodified silica supports.
Langmuir 28(26) , 10040-9, (2012) Silica is a highly attractive support material for protein immobilization in a wide range of biotechnological and biomedical-analytical applications. Without suitable derivatization, however, the sili... |
|
|
Phosphorolytic cleavage of sucrose by sucrose-grown ruminal bacterium Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis strain k3.
Folia Microbiol. (Praha) 55(4) , 383-5, (2010) Rumen bacterium Pseudobutyrivibrio ruminis strain k3 utilized over 90% sucrose added to the growth medium as a sole carbon source. Zymographic studies of the bacterial cell extract revealed the presen... |
|
|
Enzymatic synthesis of stable, odorless, and powdered furanone glucosides by sucrose phosphorylase.
Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 64 , 134, (2000) Sucrose phosphorylase from Leuconostoc mesenteroides catalyzed transglucosylation from sucrose to 4-hydroxy-3(2H)-furanone derivatives. When 4-hydroxy-2,5-dimethyl-3(2H)-furanone (HDMF) and 2-ethyl-4-... |
| 1-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]-1H-indole |
| 1-[(4-Methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]-1H-indole |
| 1H-Indole, 1-[(4-methylphenyl)sulfonyl]-3-[4-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]- |
| MFCD00132397 |


