丙酰胺
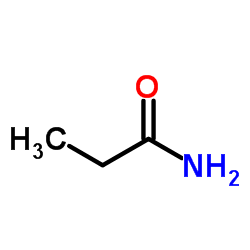
丙酰胺结构式

|
常用名 | 丙酰胺 | 英文名 | Propionamide |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS号 | 79-05-0 | 分子量 | 73.094 | |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 | 沸点 | 103.0±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| 分子式 | C3H7NO | 熔点 | 79 °C | |
| MSDS | 中文版 美版 | 闪点 | 16.1±22.6 °C | |
| 符号 |

GHS07 |
信号词 | Warning |
丙酰胺用途用途一:用于麦迪霉素药物的合成 用途二:用于有机合成。 |
| 中文名 | 丙酰胺 |
|---|---|
| 英文名 | propionamide |
| 英文别名 | 更多 |
| 密度 | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| 沸点 | 103.0±23.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| 熔点 | 79 °C |
| 分子式 | C3H7NO |
| 分子量 | 73.094 |
| 闪点 | 16.1±22.6 °C |
| 精确质量 | 73.052765 |
| PSA | 43.09000 |
| LogP | -0.38 |
| 外观性状 | 白色晶体 |
| 蒸汽压 | 18.3±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| 折射率 | 1.431 |
| 储存条件 | 本品应密封于阴凉干燥处保存。 |
| 稳定性 | 1. 存在于烟气中。 |
| 水溶解性 | SOLUBLE |
| 分子结构 | 1、 摩尔折射率:19.51 2、 摩尔体积(cm3/mol):78.8 3、 等张比容(90.2K):185.6 4、 表面张力(dyne/cm):30.6 5、 极化率(10-24cm3):7.73 |
| 计算化学 | 1.疏水参数计算参考值(XlogP):无 2.氢键供体数量:1 3.氢键受体数量:1 4.可旋转化学键数量:1 5.互变异构体数量:3 6.拓扑分子极性表面积43.1 7.重原子数量:5 8.表面电荷:0 9.复杂度:42.2 10.同位素原子数量:0 11.确定原子立构中心数量:0 12.不确定原子立构中心数量:0 13.确定化学键立构中心数量:0 14.不确定化学键立构中心数量:0 15.共价键单元数量:1 |
| 更多 | 1. 性状:白色片状结晶 2. 密度(g/mL,25/4℃):1.042 3. 相对蒸汽密度(g/mL,空气=1):不确定 4. 熔点(ºC):81.3 5. 沸点(ºC,常压):213 6. 沸点(ºC,5.2kPa):不确定 7. 折射率(n110D):1.418 8. 闪点(ºC):不确定 9. 比旋光度(º):不确定 10. 自燃点或引燃温度(ºC):不确定 11. 蒸气压(kPa,25ºC):不确定 12. 饱和蒸气压(kPa,60ºC):不确定 13. 燃烧热(KJ/mol):不确定 14. 临界温度(ºC):不确定 15. 临界压力(KPa):不确定 16. 油水(辛醇/水)分配系数的对数值:不确定 17. 爆炸上限(%,V/V):不确定 18. 爆炸下限(%,V/V):不确定 19. 溶解性:溶于水、乙醇、乙醚和氯仿。能随水蒸气挥发 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 丙酰胺上游产品 9 | |
|---|---|
| 丙酰胺下游产品 10 | |
| 海关编码 | 2924299036 |
|---|---|
| 中文概述 | HS:2924299036 灭草隆、灭幼脲、炔苯酰草胺等〔包括麦锈灵、棉胺宁、灭草灵、炔草隆、杀草胺〕 增值税率:17.0% 退税率:9.0% 监管条件:S 最低关税:6.5% 普通关税:30.0% |
| 申报要素 | 品名, 成分含量, 用途, 包装 |
| 监管条件 | S.进出口农药登记证明 |
| Summary | HS:2924299036 propionamide VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:S MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Ethyl acetate extract from Glycosmis parva leaf induces apoptosis and cell-cycle arrest by decreasing expression of COX-2 and altering BCL-2 family gene expression in human colorectal cancer HT-29 cells.
Pharm. Biol. 53(4) , 540-7, (2015) Glycosmis parva Craib (Rutaceae) is reported to have cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities by decreasing COX-2 expression.To investigate the effect of G. parva on human colorectal cancer cells ex... |
|
|
Gamma secretase inhibitors enhance vincristine-induced apoptosis in T-ALL in a NOTCH-independent manner.
Apoptosis 19(11) , 1616-26, (2014) Activating mutations in the NOTCH1 gene are found in over 50 % of T-ALL cases. Since Notch signaling contributes to the leukemia cell survival and growth, targeting Notch signaling using γ-secretase i... |
|
|
Mass spectrometric characterization of glucuronides formed by a new concept, combining Cunninghamella elegans with TEMPO.
J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 84 , 278-84, (2013) A new concept for the production of drug glucuronides is presented and the products formed were characterized using ultra high performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (UPLC... |
| Propionimidic acid |
| Carbylamine, ethyl- |
| Propanimidic acid (VAN) |
| Ethylcarbylamine |
| n-propylamide |
| MONOMETHYLACETAMIDE |
| Propionamide |
| Propylamide |
| Propionimidic acid (VAN) |
| Propanimidic acid |
| carboxylic acid methyl amide |
| MFCD00008039 |
| methylacetamide |
| Ethylformamide |
| Methyl acetamide |
| Propionic acid amide |
| propionylamine |
| EINECS 201-172-1 |
| Propanamide |
| Acetamide, methyl- |
| propionic amide |

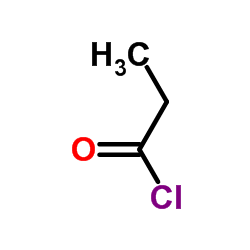 CAS号79-03-8
CAS号79-03-8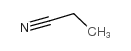 CAS号107-12-0
CAS号107-12-0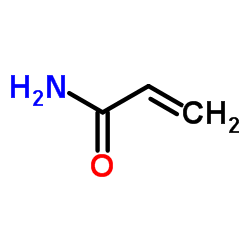 CAS号79-06-1
CAS号79-06-1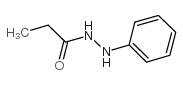 CAS号20730-02-3
CAS号20730-02-3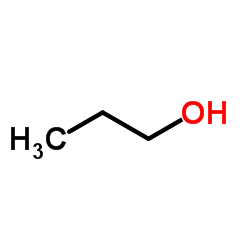 CAS号71-23-8
CAS号71-23-8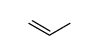 CAS号187737-37-7
CAS号187737-37-7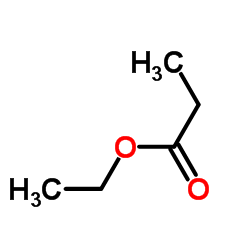 CAS号105-37-3
CAS号105-37-3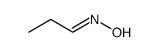 CAS号627-39-4
CAS号627-39-4 CAS号107-03-9
CAS号107-03-9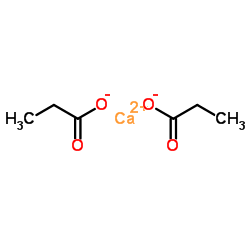 CAS号4075-81-4
CAS号4075-81-4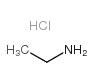 CAS号557-66-4
CAS号557-66-4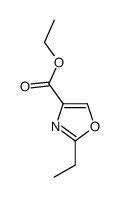 CAS号145936-64-7
CAS号145936-64-7 CAS号19961-53-6
CAS号19961-53-6 CAS号104-53-0
CAS号104-53-0 CAS号10264-24-1
CAS号10264-24-1 CAS号554-12-1
CAS号554-12-1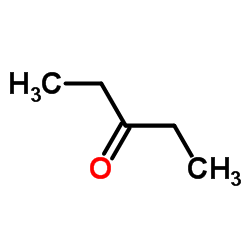 CAS号96-22-0
CAS号96-22-0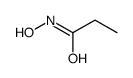 CAS号2580-63-4
CAS号2580-63-4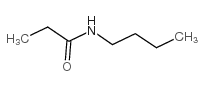 CAS号2955-67-1
CAS号2955-67-1
