Quartz-crystal microbalance-dissipation technique for the study of initial adsorption of fibronectin onto tresyl chloride-activated titanium.
T Hayakawa, M Yoshinari, K Nemoto
文献索引:J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B. Appl. Biomater. 73(2) , 271-6, (2005)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The immobilization of cell-adhesive proteins onto titanium implants improves biological response at the implant-tissue interface. Previous studies demonstrated the easy and direct attachment of fibronectin onto titanium with the use of a 2,2,2-trifluoroethanesulfonyl chloride (tresyl chloride) activation technique. The present study investigated the initial adsorption behavior of fibronectin on tresyl chloride-activated titanium by the quartz-crystal microbalance-dissipation (QCM-D) technique. The crystal resonant frequency and the dissipation shift of the oscillator were simultaneously measured by the injection of fibronectin/phosphate-buffered saline solution (pH = 7.4). The tresyl chloride-activated titanium surface showed a faster and greater decrease in frequency than that of untreated titanium, indicating that a greater amount of fibronectin was adsorbed in the former case during a 120-min adsorption. The dissipation-frequency plots revealed that, during the initial stage of adsorption, the bond between fibronectin and tresyl chloride-activated titanium is stronger than that between fibronectin and untreated titanium. The QCM-D technique can provide new insights into the adsorption mechanism of fibronectin.(c) 2005 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
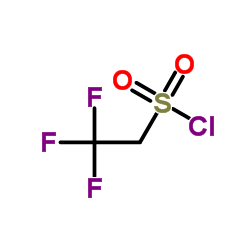 |
2,2,2-三氟乙基磺酰氯
CAS:1648-99-3 |
C2H2ClF3O2S |
|
Tresyl-based conjugation of protein antigen to lipid nanopar...
2010-01-01 [Int. J. Pharm. 401(1-2) , 87-92, (2010)] |
|
Compared stability of Sepharose-based immunoadsorbents prepa...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 584(1) , 17-22, (1992)] |
|
Multifunctional commercially pure titanium for the improveme...
2016-03-01 [Mater. Sci. Eng. C. Mater. Biol. Appl. 60 , 384-93, (2015)] |
|
Tresyl-mediated synthesis: kinetics of competing coupling an...
1999-01-01 [Bioconjug. Chem. 10(2) , 213-20, (1999)] |
|
Receptor-specific targeting with liposomes in vitro based on...
2009-03-01 [Pharm. Res. 26(3) , 529-38, (2009)] |