Existence of postsynaptic dopamine D2 receptor as an enhancer of contractile response in vas deferens.
H Morishita, T Katsuragi
文献索引:Eur. J. Pharmacol. 344(2-3) , 223-9, (1998)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Effects of dopamine and (+/-)-2-(N-phenylethyl-N-propyl)amino-5-hydroxy-tetralin hydrochloride (N-0434), a dopamine D2 receptor agonist, in the presence of prazosin on the ATP- and acetylcholine-induced contraction were investigated in the guinea-pig vas deferens in order to test for the existence of postsynaptic dopamine receptors. The contraction induced by ATP was potentiated by dopamine and N-0434. This potentiation was antagonized by spiperone, a dopamine D2 receptor antagonist, but not by a dopamine D1 receptor antagonist and an alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonist. Similar results were also observed by acetylcholine as well as ATP. The contraction induced by transmural nerve stimulation in the presence of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists was also potentiated by N-0434, and this potentiation was antagonized by spiperone. The results suggest that dopamine D2 receptors are located on the postsynaptic site of guinea-pig vas deferens and that the contractile responses to ATP and acetylcholine are potentiated via activation of dopamine D2 receptor.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
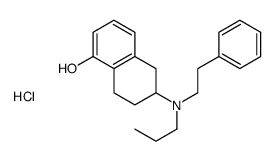 |
(±)-PPHT盐酸盐
CAS:71787-90-1 |
C21H28ClNO |
|
Differential effects of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor agonists...
1995-04-01 [J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 273 , 40, (1995)] |
|
Multiple fluorescent ligands for dopamine receptors. I. Phar...
1991-05-03 [Brain Res. 547(2) , 199-207, (1991)] |
|
Relations between the extracellular concentrations of cholin...
1997-09-01 [J. Neurochem. 69(3) , 1246-51, (1997)] |
|
Biphasic effects of dopamine agonist N-0434 on locomotor beh...
1993-04-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 44(4) , 865-8, (1993)] |
|
Adenylate cyclase from sea urchin eggs is positively and neg...
1992-12-01 [Exp. Cell Res. 203(2) , 491-4, (1992)] |