L-type Ca2+ channel antagonists block voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in identified leech neurons.
Paul Wilhelm Dierkes, Verena Wende, Peter Hochstrate, Wolf-Rüdiger Schlue
文献索引:Brain Res. 1013(2) , 159-67, (2004)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
We investigated the effect of L-type Ca2+ channel antagonists on the Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in leech Retzius, Leydig, AP, AE, P, and N neurons. The efficacy of the antagonists was quantified by monitoring their effect on the increase in the intracellular free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i; measured by Fura-2) that was induced by depolarizing the cell membrane by raising the extracellular K+ concentration. This K+-induced [Ca2+]i increase was blocked by the phenylalkylamines verapamil, gallopamil, and devapamil, the benzothiazepine diltiazem, as well as by the 1,4-dihydropyridine nifedipine. The blocking effect of the three phenylalkylamines was similar, being most pronounced in P and N neurons and smaller in Leydig, Retzius, AP, and AE neurons. Contrastingly, diltiazem and nifedipine were similarly effective in the neurons investigated, whereby their efficacy was like that of the phenylalkylamines in Retzius, Leydig, AP, and AE neurons. Depending on cell type and blocking agent, the concentrations necessary to suppress the K+-induced [Ca2+]i increase by 50% were estimated to vary between 5 and 190 microM. At high concentrations, the phenylalkylamines and diltiazem by themselves caused a marked [Ca2+]i increase in Leydig, P, and N neurons, which is probably due to activation of the caffeine-sensitive ion channels present in the plasma membrane of these cells. Together with previous observations, the results indicate a distant relationship of the voltage-gated Ca2+ channels present in many if not all leech neurons to vertebrate L-type Ca2+ channels.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
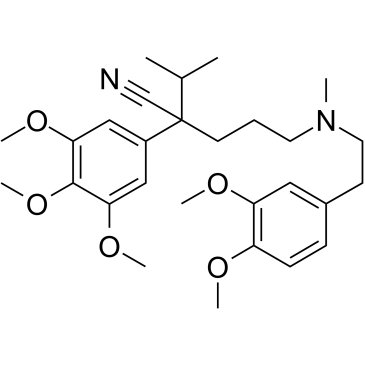 |
戈洛帕米
CAS:16662-47-8 |
C28H40N2O5 |
|
Force response to stretches in activated frog muscle fibres ...
2003-01-01 [Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 538 , 429-38; discussion 438-9, (2003)] |
|
Ca2+ pathway involved in the refilling of store sites in rat...
2009-04-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 296(4) , C889-99, (2009)] |
|
Effects of phenylalkylamines and benzothiazepines on Ca(v)1....
2007-11-14 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 573(1-3) , 39-48, (2007)] |
|
Insulin stimulates Ca2+ uptake via PKC, cAMP, and p38 MAPK i...
2005-05-06 [Life Sci. 76(25) , 2903-19, (2005)] |
|
A selective beta2-adrenergic agonist, terbutaline, improves ...
2006-07-24 [Life Sci. 79(9) , 905-12, (2006)] |