Construction of a microprocessor-controlled pulsed quench-flow apparatus for the study of fast chemical and biochemical reactions.
J Langowski, C Urbanke, E Schuppe
文献索引:Anal. Biochem. 142(1) , 91-7, (1984)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The construction and operation of a microprocessor-controlled quenched-flow machine are described. Two sets of syringes are moved by high-torque stepping motors to achieve any desired mixing scheme. The dead time of the instrument is pulsed quench-flow operation is of the order of 10 ms. The fastest possible reaction time is 12 ms with the reaction chamber used here; this might be extended downward with other reaction chambers. The reactant volume required is low; 1 ml of solution for each reactant is sufficient for more than 40 kinetic measurements. The machine is tested by alkaline hydrolysis of 2,4-dinitrophenylacetate and used in the investigation of the reaction mechanism of the EcoRI restriction endonuclease and of GTPase activity of ribosomes.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
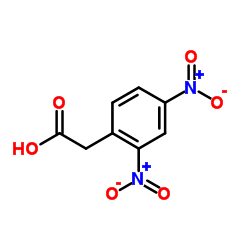 |
2,4-二硝基苯乙酸
CAS:643-43-6 |
C8H6N2O6 |
|
A reinvestigation of the pre-steady-state ATPase activity of...
1992-09-01 [Eur. J. Biochem. 208(2) , 289-94, (1992)] |
|
Synthesis of a parabactin photoaffinity label. Bergeron RJ, ...
[J. Org. Chem. 52(1) , 144-49, (1987)] |
|
The coupling of diazonium salts with aliphatic carbon atoms....
[Org. React. , (1959)] |
|
A self-assembled nanofiber catalyst for ester hydrolysis.
2007-10-10 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 129(40) , 12082-3, (2007)] |
|
A simple rapid mixing device.
1980-07-15 [Anal. Biochem. 106(1) , 73-7, (1980)] |