Boldenone, boldione, and milk replacers in the diet of veal calves: the effects of phytosterol content on the urinary excretion of boldenone metabolites.
G Gallina, G Ferretti, R Merlanti, C Civitareale, F Capolongo, R Draisci, C Montesissa
文献索引:J. Agric. Food Chem. 55(20) , 8275-83, (2007)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Twenty-six veal calves were split into two groups and fed two milk replacers with a different content of phytosterols for 26 days; then, 14 calves (7 animals from each diet) were kept as controls and 12 calves (6 per diet) received daily, per os, a combination of 17beta-boldenone (17beta-Bol) and androsta-1,4-dien-3,17-dione (ADD) for 38 days. The urinary elimination of 17 alpha-/17beta-boldenone conjugates (17 alpha/beta-Bol) and androsta-1,4-dien-3,17-dione (ADD) was followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry from all of the animals until slaughtering. In urine from treated animals, 17 alpha-Bol concentrations, despite a great variability, were greater than 17beta-Bol, both detected always as conjugates. At days 1, 2, and 3, the mean urine concentration of 17 alpha-Bol was higher than 12 ng/mL. A remarkable decrease was observed during the following days, but the 17 alpha-Bol concentration was still higher than the attention level of 2 ng/mL in 58% of the samples; the concentration of 17beta-Bol was around the action level of 1 ng/mL; two days after treatment withdrawal, no 17beta-Bol was detected in the urine. In urine from control animals, the 17 alpha-Bol concentration was strictly related to the phytosterol content of the diet, while, in urine from treated animals, the much higher 17 alpha-Bol levels were not modified by the production from diet precursors. The results confirmed that a 17 alpha-Bol level higher than 2 ng/mL should be considered as evidence of suspected illegal treatment and that the urinary excretion of 17beta-Bol is due to exogenous administration of 17beta-Bol. The discontinuous rate of elimination of both 17 alpha- and 17beta-Bol, despite the daily administration of 17beta-Bol plus ADD, indicates the necessity for further research to detect other urinary boldenone metabolites to strength surveillance strategy.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
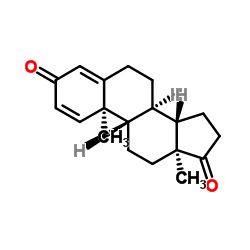 |
1,4-雄烯二酮
CAS:897-06-3 |
C19H24O2 |
|
Development of a quantitative method for the simultaneous an...
2000-02-01 [Food Chem. 187 , 120-9, (2015)] |
|
Cholesterol assimilation and biotransformation by Lactobacil...
2012-01-01 [Biotechnol. Lett. 34(1) , 103-7, (2012)] |
|
Evaluation of urinary excretion of androgens conjugated to c...
2014-01-01 [J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 139 , 192-200, (2014)] |
|
Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin alters growth, activity and cell en...
2007-06-01 [Microbiology 153(Pt 6) , 1981-92, (2007)] |
|
Comparative analysis of genes encoding key steroid core oxid...
2013-11-01 [J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 138 , 41-53, (2013)] |