Mechanism-based in vivo inactivation of lauric acid hydroxylases.
C A CaJacob, P R Ortiz de Montellano
文献索引:Biochemistry 25(16) , 4705-11, (1986)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The hepatic cytochrome P-450 isozymes that catalyze omega- and (omega - 1)-hydroxylation of lauric acid are specifically inactivated in vitro but not in vivo by 10-undecynoic acid. The lack of in vivo activity may result from rapid degradation of the inhibitor by beta-oxidation. Strategies for the construction of fatty acid analogues that retain the ability to inactivate fatty acid hydroxylases but are resistant to metabolic degradation have therefore been sought. Fatty acid analogues in which the carboxylic acid group is replaced by a sulfate moiety, or in which two methyl groups are placed vicinal to the carboxylic acid group, have been found to inactivate lauric acid hydroxylases in vitro and in vivo without causing time-dependent inhibition of ethoxycoumarin O-deethylation or N-methyl-p-chloroaniline N-demethylation.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
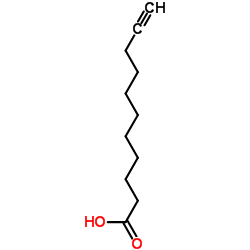 |
10-十一碳炔酸
CAS:2777-65-3 |
C11H18O2 |
|
Simultaneous electropolymerization and electro-click functio...
2014-05-27 [ACS Nano 8(5) , 5240-8, (2014)] |
|
Amphiphilic polyesters derived from silylated and germylated...
2009-04-13 [Biomacromolecules 10(4) , 850-7, (2009)] |
|
Cellulose/water: liquid/gas and liquid/liquid phase equilibr...
2007-06-01 [Biomacromolecules 8(6) , 1865-72, (2007)] |
|
10-Undecynoic acid, an inhibitor of cytochrome P450 4A1, inh...
1999-01-01 [Acta Biochim. Pol. 46(1) , 203-10, (1999)] |
|
Specific inactivation of hepatic fatty acid hydroxylases by ...
1984-04-10 [J. Biol. Chem. 259(7) , 4136-41, (1984)] |