Protective effect of 4',5-dihydroxy-3',6,7-trimethoxyflavone from Artemisia asiatica against Abeta-induced oxidative stress in PC12 cells.
H J Heo, H Y Cho, B Hong, H K Kim, E K Kim, B G Kim, D H Shin
文献索引:Amyloid 8(3) , 194-201, (2001)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Amyloid beta protein (Abeta)-induced free radical-mediated neurotoxicity is a leading hypothesis as a cause of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Abeta increased free radical production and lipid peroxidation in PC12 nerve cells, leading to apoptosis and cell death. The effect of 4',5-dihydroxy-3',6,7-trimethoxyflavone from Artemisia asiatica on Abeta induced neurotoxicity was investigated using PC12 cells. Pretreatment with isolated 4',5-dihydroxy-3',6,7-trimethoxyflavone and vitamin E prevented the Abeta-induced reactive oxygen species (ROS). The 4',5-dihydroxy-3',6,7-trimethoxyflavone resulted in concentration-dependant decreased Abeta toxicity assessed by 3-(4, 5- dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. However, treatment with these antioxidants inhibited the Abeta-induced neurotoxic effect. Therefore, these results indicate that micromolecular Abeta-induced oxidative cell stress is reduced by 4,5-dihydroxy-3',6,7-trimethoxyflavone from Artemisia asiatica.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
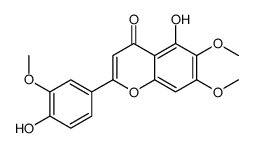 |
3′-甲氧基蓟黄素
CAS:41365-32-6 |
C18H16O7 |
|
[Determination of flavonoids in buds of Herba Artemisiae Sco...
2005-04-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 30(8) , 591-4, (2005)] |
|
Analysis of vervain flavonoids by HPLC/Diode array detector ...
1999-11-01 [J. Agric. Food Chem. 47(11) , 4579-82, (1999)] |
|
[Studies on chemical constituents in buds of Artemisia scopa...
2002-03-01 [Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 27(3) , 202-4, (2002)] |
|
Two flavonoids from Artemisia herba-alba Asso with in vitro ...
2005-05-13 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 99(1) , 145-6, (2005)] |
|
[Flavones isolated from Thymus carnosus Boiss].
1987-01-01 [Ann. Pharm. Fr. 45(6) , 467-70, (1987)] |