Comparison of 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl and 9-fluoreneacetyl-tagged silica-based derivatization reagents in high-performance liquid chromatography.
H M Zhang, F X Zhou, I S Krull
文献索引:J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 10(8) , 577-86, (1992)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Two silica reagents based on a 4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzoyl backbone were synthesized and characterized with 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl (FMOC) and 9-fluoreneacetyl (FA) tags. These reagents were tested by derivatization of primary and secondary amines. Derivatization conditions such as temperature, time and triethylamine catalyst were tested. The FA-tagged silica reagent showed better performance than the FMOC-tagged silica reagent by a comparison of derivatization efficiencies, stabilities of reagents, and blank reagent interferences with derivatization. Finally, cadaverine and an aliphatic amine mixture were analysed using the FA-tagged reagent by pre-column, off-line derivatization and fluorescence detection.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
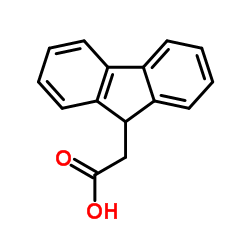 |
9-芴乙酸
CAS:6284-80-6 |
C15H12O2 |
|
Structural basis for the potent calpain inhibitory activity ...
2008-07-24 [J. Med. Chem. 51(14) , 4346-50, (2008)] |
|
Prolonged pheromonotropic activity of pseudopeptide mimics o...
1997-10-31 [Regul. Pept. 72(2-3) , 161-7, (1997)] |
|
Direct determination of adamantanamine in plasma and urine w...
[J. Chromatogr. A. 619(1) , 93-101, (1993)] |
|
Molecular modeling studies of the binding modes of aldose re...
1998-10-01 [Bioorg. Med. Chem. 6(10) , 1811-9, (1998)] |
|
Automated HPLC analyses of drugs of abuse via direct injecti...
1994-01-01 [Biomed. Chromatogr. 8(2) , 53-62, (1994)] |