Ginsenoside Rd protects neurons against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity by inhibiting ca(2+) influx.
Chen Zhang, Fang Du, Ming Shi, Ruidong Ye, Haoran Cheng, Junliang Han, Lei Ma, Rong Cao, Zhiren Rao, Gang Zhao
文献索引:Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 32(1) , 121-8, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Our previous studies have demonstrated that ginsenoside Rd (GSRd), one of the principal ingredients of Pana notoginseng, has neuroprotective effects against ischemic stroke. However, the possible mechanism(s) underlying the neuroprotection of GSRd is/are still largely unknown. In this study, we treated glutamate-injured cultured rat hippocampal neurons with different concentrations of GSRd, and then examined the changes in neuronal apoptosis and intracellular free Ca(2+) concentration. Our MTT assay showed that GSRd significantly increased the survival of neurons injured by glutamate in a dose-dependent manner. Consistently, TUNEL and Caspase-3 staining showed that GSRd attenuated glutamate-induced cell death. Furthermore, calcium imaging assay revealed that GSRd significantly attenuated the glutamate-induced increase of intracellular free Ca(2+) and also inhibited NMDA-triggered Ca(2+) influx. Thus, the present study demonstrates that GSRd protects the cultured hippocampal neurons against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity, and that this neuroprotective effect may result from the inhibitory effects of GSRd on Ca(2+) influx.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
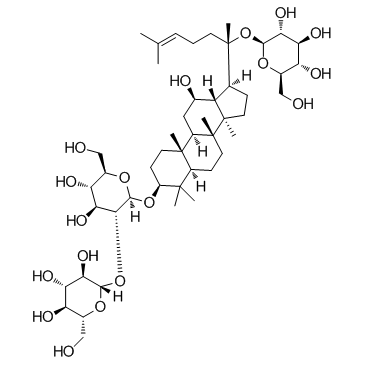 |
人参皂苷Rd
CAS:52705-93-8 |
C48H82O18 |
|
Transcriptome analysis of Panax vietnamensis var. fuscidicus...
2015-01-01 [BMC Genomics 16 , 159, (2015)] |
|
Protective effects of ginsenoside Rd on PC12 cells against h...
2008-10-01 [Biol. Pharm. Bull. 31(10) , 1923-7, (2008)] |
|
Bioconversion of ginsenoside Rc into Rd by a novel α-L-arabi...
2013-04-01 [Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103(4) , 747-54, (2013)] |
|
Ginsenoside Rd attenuates early oxidative damage and sequent...
2011-02-01 [Neurochem. Int. 58(3) , 391-8, (2011)] |
|
Highly selective microbial transformation of major ginsenosi...
2012-10-01 [J. Appl. Microbiol. 113(4) , 807-14, (2012)] |