Volume sensitive efflux of taurine in HEK293 cells overexpressing phospholemman.
M Morales-Mulia, H Pasantes-Morales, J Morán
文献索引:Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1496(2-3) , 252-60, (2000)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The role of the phospholemman (PLM) on the efflux of taurine and chloride induced by swelling was studied in HEK293 cells overexpressing stable transfected PLM. PLM, a substrate for protein kinases C and A, is a protein that induces an anion current in Xenopus oocytes and forms taurine-selective channels in lipid bilayers. Taurine contributes as an osmolyte to regulatory volume decrease (RVD) and is highly permeable through PLM channels in bilayers. In PLM-overexpressing cells the process of RVD was more rapid and efficient (75%) than in control cells (44%). Also, [(3)H]taurine and (125)I efflux induced by hyposmolarity were markedly increased (30-100%) in two subclones of cells overexpressing PLM. This increased efflux was sensitive to the Cl channel blockers DDF, NPPB and DIDS. Acute treatment of control cells with isoproterenol and norepinephrine induced a significant potentiation (50-60%) of [(3)H]taurine release induced by hyposmolarity. In PLM-overexpressing cells the potentiation by these drugs was higher (100%). Insulin induced also an increase in [(3)H]taurine release, but only in PLM-overexpressing cells (50%). These results indicate that PLM may play a role in the RVD and that its phosphorylation may have a physiological significance during this process. The mechanisms involved in this process could include the activation of PLM itself as channel or the modulation of other preexisting channels.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
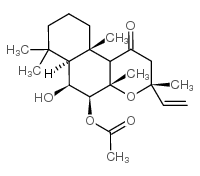 |
福斯高林1,9-二脱氧
CAS:64657-18-7 |
C22H34O5 |
|
Roles of calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II in long-term...
2014-01-01 [PLoS ONE 9(9) , e107442, (2014)] |
|
Inhibition of Akt reverses the acquired resistance to sorafe...
2014-06-01 [Mol. Cancer Ther. 13(6) , 1589-98, (2014)] |
|
The expression and regulation of depolarization-activated K+...
2001-04-01 [Pflugers Arch. 442(1) , 49-56, (2001)] |
|
Effect of protein kinase A-induced phosphorylation on the ga...
1999-07-01 [Biophys. J. 77(1) , 204-16, (1999)] |
|
Synthetic transformation of ptychantin into forskolin and 1,...
2006-06-09 [J. Org. Chem. 71(12) , 4619-24, (2006)] |