| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
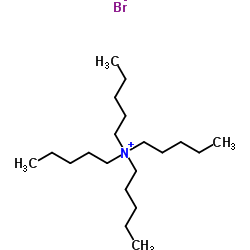 |
四戊基溴化铵
CAS:866-97-7 |
|
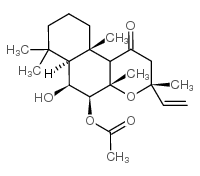 |
福斯高林1,9-二脱氧
CAS:64657-18-7 |
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|
 |
四戊基溴化铵
CAS:866-97-7 |
|
 |
福斯高林1,9-二脱氧
CAS:64657-18-7 |