Discordant varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein C expression and localization between cultured cells and human skin vesicles.
Johnathan Storlie, John E Carpenter, Wallen Jackson, Charles Grose
文献索引:Virology 382(2) , 171-81, (2008)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Because of its very low titer, varicella-zoster virus (VZV) infectivity is usually transferred by passage of trypsin dispersed infected cells. Previously, we observed that gC biosynthesis was markedly delayed in monolayers inoculated with cell free virus. In this report, we investigated the kinetics of gC expression in more detail and included studies of monolayers inoculated with trypsin dispersed infected cells, the more traditional method of VZV infection. Extensive imaging analyses disclosed that gC was detectable in some inoculum cells, but little gC biosynthesis occurred during the first 48 hpi in the newly infected underlying monolayer. In contrast, during the first 24-48 hpi, expression of VZV gE and gB was easily detectable. Using real-time RT-PCR, we found a delay in accumulation of VZV gC transcripts that paralleled the delay in expression of VZV gC protein. Treatment with hexamethylene bisacetamide (HMBA) increased expression of both gC protein and gC mRNA. HMBA treatment also increased virus titer by 4-fold, but paradoxically reduced plaque size in the titration assay. Finally, we examined skin vesicles from cases of chickenpox and zoster in humans and observed abundant amounts of gC expression. In short, this report documents an unexpected delay in both gC mRNA and protein production under all conditions of VZV infection of cultured cells.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
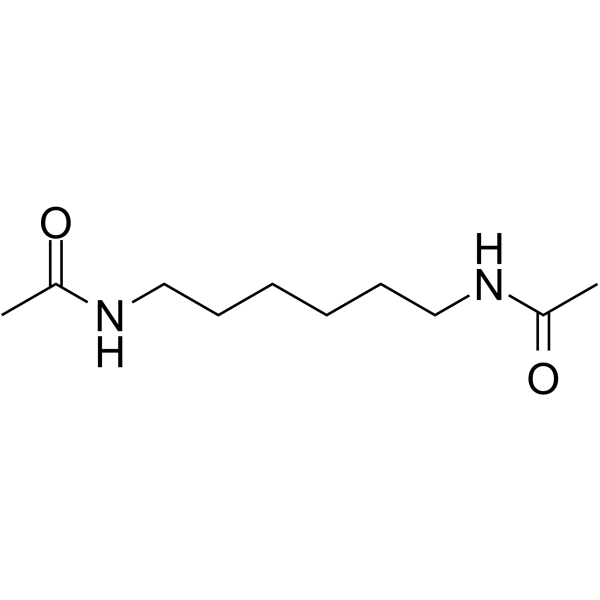 |
N,N'-六亚甲基双乙酰胺
CAS:3073-59-4 |
C10H20N2O2 |
|
Balancing polymer hydrophobicity for ligand presentation and...
2015-07-01 [Biomater. Sci. 3 , 1114-23, (2015)] |
|
Thioredoxin-interacting protein regulates the differentiatio...
2015-05-01 [Exp. Hematol. 43 , 393-403.e2, (2015)] |
|
Cellular Protein WDR11 Interacts with Specific Herpes Simple...
2015-10-01 [J. Virol. 89 , 9841-52, (2015)] |
|
Genetic manipulation of RPS5 gene expression modulates the i...
2015-07-01 [Int. J. Oncol. 47 , 303-14, (2015)] |
|
Acute hypoxia affects P-TEFb through HDAC3 and HEXIM1-depend...
2014-08-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 42(14) , 8954-69, (2014)] |