Advanced glycation end-products inhibition improves endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis.
Ashit Syngle, Kanchan Vohra, Nidhi Garg, Ladbans Kaur, Prem Chand
文献索引:Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 15(1) , 45-55, (2012)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with vascular endothelial dysfunction. The objective was to study the efficacy and safety of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) inhibitor (benfotiamine 50 mg + pyridoxamine 50 mg + methylcobalamin 500 μg, Vonder(®) (ACME Lifescience, Baddi, Himachal Pradesh, India)) on endothelial function in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).Twenty-four patients with established active RA with high disease activity (Disease Activity Score of 28 joints [DAS28 score] > 5.1) despite treatment with stable doses of conventional disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs were investigated. Inflammatory disease activity (DAS28 and Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index [HAQ-DI] scores, erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR] and C-reactive protein [CRP]), markers of endothelial dysfunction, serum nitrite concentration and endothelium-dependent and -independent vasodilation of the brachial artery were measured before and after 12 weeks therapy with twice a day oral AGEs inhibitor.After treatment, flow-mediated vasodilation improved from 9.64 ± 0.65% to 15.82 ± 1.02% (P < 0.01), whereas there was no significant change in endothelium-independent vasodilation with nitroglycerin and baseline diameter; serum nitrite concentration significantly reduced from 5.6 ± 0.13 to 5.1 ± 0.14 μmol/L (P = 0.004), ESR from 63.00 ± 3.5 to 28.08 ± 1.5 mm in the first h (P < 0.01) and CRP levels from 16.7 ± 4.1 to 10.74 ± 2.9 mg/dL (P < 0.01). DAS28 and HAQ-DI scores were significantly reduced, from 5.9 ± 0.17 to 3.9 ± 0.17 (P < 0.01) and 4.6 ± 0.17 to 1.7 ± 0.22 (P < 0.01), respectively.Advanced glycation end products inhibitor improves endothelial dysfunction and inflammatory disease activity in RA. In RA, endothelial dysfunction is part of the disease process and is mediated by AGEs-induced inflammation.© 2011 The Authors. International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases © 2011 Asia Pacific League of Associations for Rheumatology and Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
甲钴胺
CAS:13422-55-4 |
C63H91CoN13O14P | |
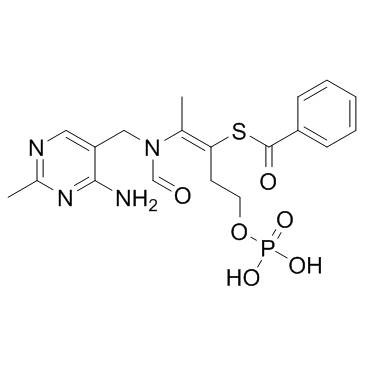 |
苯磷硫胺
CAS:22457-89-2 |
C19H23N4O6PS |
|
Environmental fate of the next generation refrigerant 2,3,3,...
2014-11-18 [Environ. Sci. Technol. 48(22) , 13181-7, (2014)] |
|
Thin-layer chromatography combined with diode laser thermal ...
2014-10-17 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1364 , 271-5, (2014)] |
|
Processing of alkylcobalamins in mammalian cells: A role for...
2009-08-01 [Mol. Genet. Metab. 97 , 260-266, (2009)] |
|
Vitamin B12-derivatives-enzyme cofactors and ligands of prot...
2011-08-01 [Chem. Soc. Rev. 40 , 4346-4363, (2011)] |
|
B12 trafficking in mammals: A for coenzyme escort service.
2006-04-25 [ACS Chem. Biol. 1 , 149-159, (2006)] |