The effect of physical and chemical treatment on the mechanical properties of the cell wall of the alga Chara corallina.
Geraldine A Toole, Andrew C Smith, Keith W Waldron
文献索引:Planta 214(3) , 468-75, (2002)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
Single large internode cells of the charophyte (giant alga) Chara corallina were dissected to give sheets of cell wall, which were then notched and their mechanical properties in tension determined. The cells were subjected to a thermal treatment in excess water (cf. cooking), which had little effect on strength but increased the stiffness, contrasting with the behaviour of higher-plant tissues. Extraction in CDTA (cyclohexane-trans-1,2-diamine-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetate) or 4 M KOH reduced the strength from 17 MPa to 10 MPa, although sequential extraction in CDTA and 4 M KOH reduced the strength further to 4 MPa. The stiffness decreased from 500 MPa to 300 MPa on extraction in CDTA or 4 M KOH, while falling to 70 MPa after extraction in CDTA followed by 4 M KOH. Conventional sequential extraction in CDTA, Na2CO3 at 1 degrees C and 20 degrees C, and KOH at 0.5 M, 1 M, 2 M and 4 M caused a gradual decrease in stiffness and strength after the CDTA treatment to the same lower values. This result is in keeping with mechanical properties for plant tissues, but in contrast to the removal of pectic polysaccharides from model cell wall systems, which does not reduce the stiffness.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
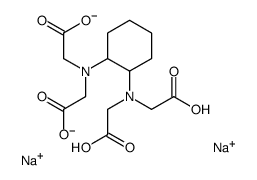 |
DCTA 钠盐
CAS:5786-78-7 |
C14H20N2Na2O8 |
|
Determination of synthetic ferric chelates used as fertilize...
2007-01-01 [J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 18(1) , 37-47, (2007)] |
|
Capillary electrophoretic-ultraviolet method for the separat...
2007-01-01 [J. AOAC Int. 90(3) , 834-7, (2007)] |
|
Detailed spectroscopic, thermodynamic, and kinetic studies o...
2009-08-17 [Inorg. Chem. 48(16) , 7864-84, (2009)] |
|
Kinetic studies on the oxidation of cytochrome b(5) Phe35 mu...
2002-04-01 [J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 7(4-5) , 375-83, (2002)] |
|
Direct magnetic resonance evidence for peroxymonocarbonate i...
2009-05-22 [J. Biol. Chem. 284(21) , 14618-27, (2009)] |