Mutagenic effects of nitrogen dioxide combined with methylurea and ethylurea in Drosophila melanogaster.
H Inoue, A Fukunaga, S Okubo
文献索引:Mutat. Res. 88(3) , 281-90, (1981)
全文:HTML全文
摘要
The standard sex-linked recessive lethal test was used to test whether NO2 induces lethal mutations in male germ cells of Drosophila in the presence or absence of alkylureas. Methylurea, ethylurea and NO2 alone did not enhance the mutation frequency significantly. However, highly significant enhancement in the mutation frequency was observed when adult flies were exposed to NO2 (150--280 ppm) for 3 h after ingestion of methylurea (0.1 M) or ethylurea (0.1 M) for 2 days. Oral administration of ethylnitrosourea and also of methylurea or ethylurea that had been exposed to NO2 in vitro were more effective in increasing the mutation frequency than methylurea or ethylurea combined in vivo with NO2. These results suggest that ingested alkylurea is converted in vivo by inhaled NO2 to highly mutagenic nitrosoalkylurea and/or other mutagens. No significant enhancement of the mutation frequency was observed when flies were fed on methylurea solution after they had been exposed to NO2.
相关化合物
| 结构式 | 名称/CAS号 | 分子式 | 全部文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
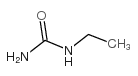 |
乙基脲
CAS:625-52-5 |
C3H8N2O |
|
Solvation of human serum albumin in aqueous alkylurea soluti...
1993-10-01 [Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 42(4) , 320-5, (1993)] |
|
Inhibition of HIV-1 infection by alkylureas.
1991-12-01 [AIDS 5(12) , 1447-52, (1991)] |
|
Neoplasia induced in male rats fed lead acetate, ethyl urea,...
1985-01-01 [Toxicol. Pathol. 13(1) , 50-7, (1985)] |
|
Comparison of nicotinamide, ethylurea and polyethylene glyco...
1997-10-01 [Chem. Pharm. Bull. 45(10) , 1688-93, (1997)] |
|
Alterations in the reproductive performance of habrobracon f...
1981-02-01 [Mutat. Res. 88(2) , 179-89, (1981)] |